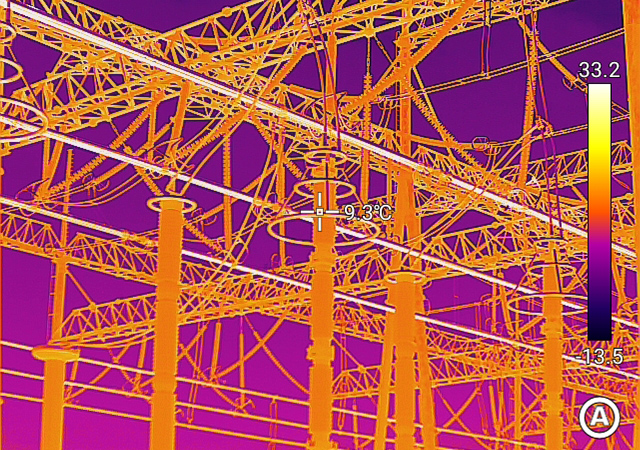
Infrared camera cores are vital tools in power maintenance, enabling maintenance technicians to detect and analyze temperature changes across high-voltage electrical equipment. By detecting hot spots and other changes in temperature, infrared camera cores can help prevent costly power outages, equipment damage, and other issues that can arise in electrical systems.
Infrared camera cores used in power maintenance are typically designed to be rugged and reliable, capable of withstanding the harsh conditions found in power plants, substations, and other high-voltage environments. They are optimized for use across a wide range of conditions, including day or night, enabling maintenance workers to effectively evaluate equipment in any lighting situation. Additionally, they can be used to safely analyze high-voltage electrical equipment without having to de-energize or shutdown the equipment.
Infrared camera cores used in power maintenance are often equipped with a laser rangefinder, which enables technicians to accurately measure the distance to electrical equipment. This feature helps to ensure accurate temperature measurements and avoid measurement errors due to distance estimation. The cores are also typically compatible with various interfaces and software platforms, allowing for the easy integration of data and analysis with existing maintenance workflows.
Incorporating the latest sensor and imaging technologies, infrared camera cores can perform high-precision temperature measurements and detect anomalies that could otherwise go unnoticed. For example, they can detect temperature variations in electrical insulation and wiring, helping detect potential fire hazards. They can also be used to detect wear on bearings, identify blockages in pipes and ducts, and evaluate insulation efficiency.
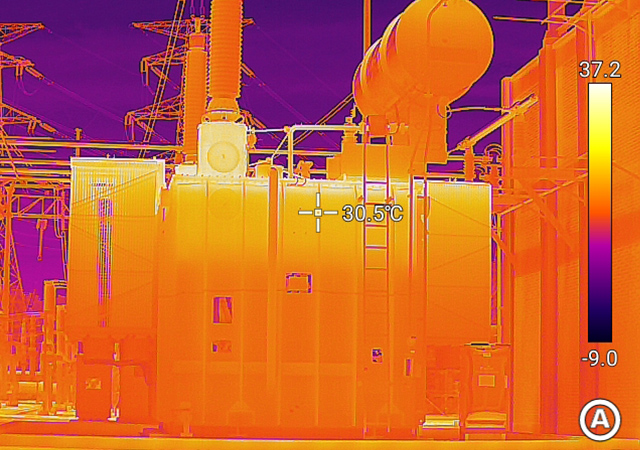

In conclusion, infrared camera cores play a vital role in power maintenance, enabling professionals to detect and diagnose potential equipment failures. They offer an efficient and cost-effective way to monitor electrical systems, identify overheating, and mitigate related hazards. By incorporating the latest technologies, these cores help keep power grids running smoothly while ensuring the safety of maintenance technicians and the surrounding communities.
Go Top