Intorduction to Infrared Detectors | GSTiR
Infrared detectors work by detecting infrared rays emitted by the human body. Infrared radiation is collected from the outside world and is concentrated on the infrared detector that converts invisible thermal radiation into electrical signal. It forms infrared thermal image for naked eye observation after magnification and image processing.
The infrared detector is the core component of the whole infrared thermal imaging system, and it is the key to detect, recognize and identify the infrared characteristic information of the target. The performance of the infrared detector directly determines the quality of the infrared thermal imaging. From different perspectives, there are many different classification methods for infrared detectors:
According to the response wavelength of infrared detector, it can be divided into short wave infrared detector (1-3μm), middle wave infrared detector (3-5μm) and long wave infrared detector (8-14μm). The above three bands are also called the three atmospheric windows of infrared.
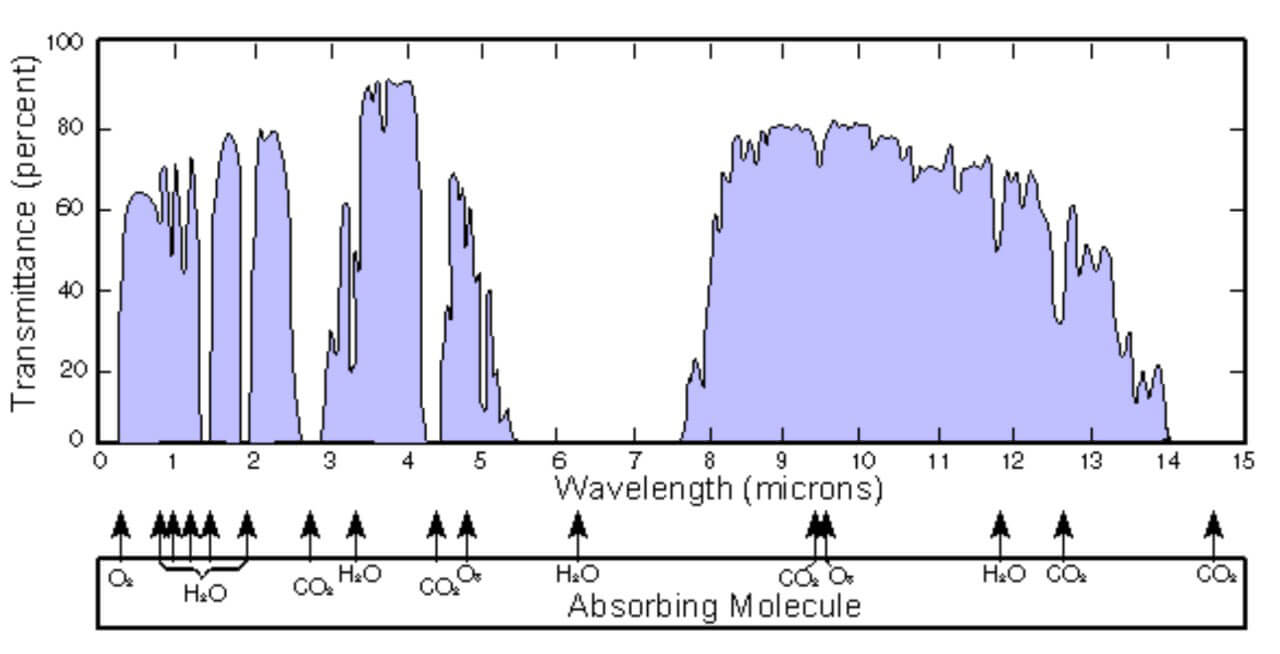
According to the infrared radiation characteristics of the target, different bands have different advantages.
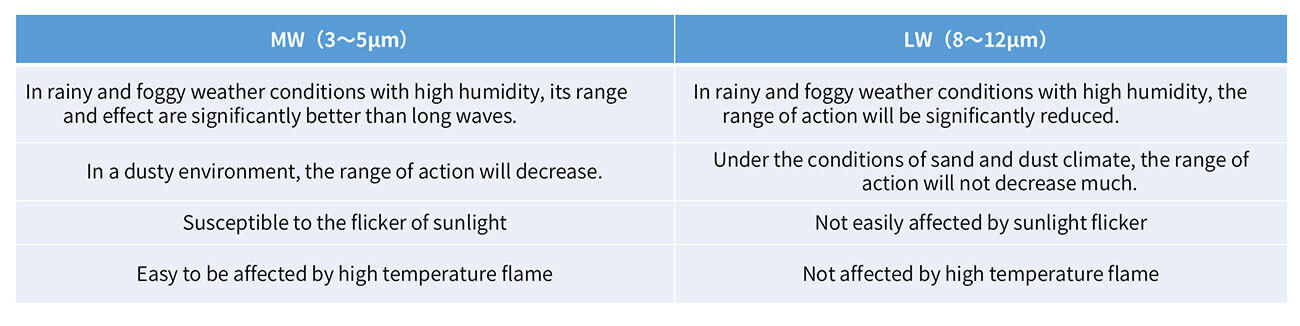
According to the working temperature, it can be divided into cooled detector and uncooled detector. General photon detectors need to work at low temperature, so they are all cooled type. However, the thermal detector generally works in the room temperature range, and the performance improvement is not obvious when the working temperature is reduced.