Array format (resolution): the number of effective pixels when the infrared detector detects the target and output a thermal image/video. The higher the resolution is, the smaller the target can be detected and the longer the detection distance is, the higher the recognition possibility of the target will be.
The detector with larger area array can:
Pixel size: pixel size refers to the actual physical size of each pixel on the detector pixel array. Smaller pixel size can integrate more pixels on the unit area of the focal plane, thus improving the resolution of the infrared detector. For the same resolution products, smaller pixel size can significantly reduce the size, weight, power consumption and cost of the detector. In addition, the detector with the same array specification and smaller pixel size can adopt shorter focal length configuration when matching the optical system to achieve the same detection and recognition efficiency, so the overall size of the system will be smaller and the cost will be better.
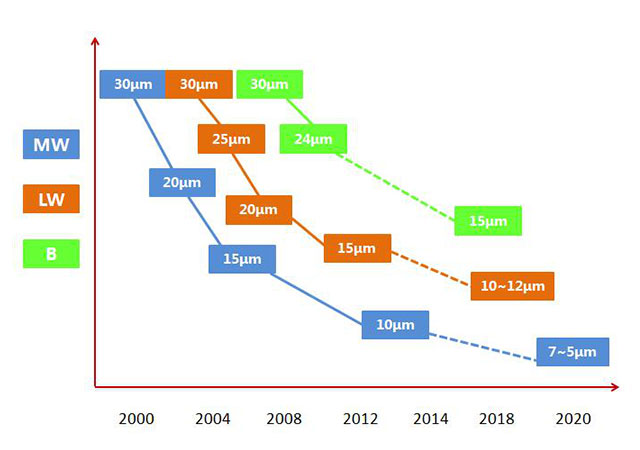
In the past 20 years, the pixel size of mainstream uncooled infrared focal plane detectors has changed from about 50um to 45um, 35um, 25um, 20um and 17 μ m, and smaller pixel sizes such as 12um and 10um have entered the substantive development and production stage.
At present, the pixel size of the cooled infrared focal plane detector has changed from about 30um to 25um, 20um, 15um and so on. Now it has gradually entered the era of 10 μ m ~ 12um as the mainstream, and the smaller pixel size such as 7 μ m ~ 5 μ m has entered the substantive development and production stage.
Noise equivalent temperature difference (NETD): when the signal-to-noise ratio of the detector is equal to 1, the temperature difference between the target and the background is an objective index to measure the sensitivity of the detector. If the temperature difference between the detection target and the background is very small, the higher the thermal sensitivity of the detector is required. The smaller the NETD value of the detector, the higher the thermal sensitivity is, the smaller the noise of the output infrared image, the better the imaging effect, and the clearer and more delicate of the image quality.
The detector with smaller NETD can make:
Frame rate:the frame rate is the number of complete images produced by the infrared thermal imager per second. If the moving speed of the measured object is very fast or the temperature changes rapidly, the infrared detector with higher frame rate should be selected, otherwise the measurement accuracy will be affected. The frame rate of some products in the industry may be limited to 9 Hz due to export restrictions. The detector products by Global Sensor Technology can achieve 25Hz ~ 50Hz, and some high frame rate products can achieve higher performance.
Go Top